

Journal of Resources and Ecology >
Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Human-Earth System in Minority Areas of Yunnan, China
Received date: 2022-09-08
Accepted date: 2023-03-30
Online published: 2024-03-14
Supported by
The National Natural Science Foundation of China(71463034)
The Joint Special Fund Project of Basic Research in Local Universities of Yunnan Province of China(202101BA070001-097)
In minority areas of Yunnan, China, the ecological environment is fragile, and social and economic development is not sufficient. The research on the evolution of human-earth systems can provide scientific guidance for solving the contradiction between environmental protection and social and economic development and promoting high-quality regional development. In this study, based on the structural division of the human-earth system, we established a comprehensive evaluation model by the data envelopment analysis (DEA) to analyze the evolution characteristics and influencing factors of the man-earth system in minority areas of Yunnan in terms of the coordinated development degree and the comprehensive efficiency of the system. The results show that: (1) From 1995 to 2020, the coordinated development degree of the human-earth system in minority areas of Yunnan showed an overall upward trend, with the average value rising from 0.31 in 1995 to 0.74 in 2020. (2) The average comprehensive efficiency of inputs and outputs of the human-earth system showed a downward trend; in particular, after 2007, the number of regions with ineffective DEA gradually increased, indicating that the development model of high inputs and consumption has not been effectively changed. (3) By calculating the system indicator weights using the entropy method, we found that the comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste, total foreign trade and urbanization rate greatly impacted the coordinated development efficiency of the human-earth system in minority areas of Yunnan.
TAI Lingjuan , YANG Hongjuan . Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Human-Earth System in Minority Areas of Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2024 , 15(2) : 372 -384 . DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2024.02.011
Fig. 1 Distribution diagram of Yunnan minority autonomous prefecture |
Table 1 Measurement indicator system of coordinated development of the human-earth system in minority areas of Yunnan |
| Subsystem | Basic indicators | Unit | Indicator attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural subsystem | Industrial wastewater discharge | 104 t | - |
| Industrial waste gas emission | 108 m3 | - | |
| Output of industrial solid waste | 104 t | - | |
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | % | + | |
| Afforestation area | 103 ha | + | |
| Economic subsystem | Investment in fixed assets | 108 yuan | + |
| Total retail sales of social consumer goods | 108 yuan | + | |
| Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita | yuan | + | |
| Total import and export volume of foreign trade | 108 USD | + | |
| Proportion of tertiary industry in GDP | % | + | |
| Social subsystem | Urbanization rate | % | + |
| Gap between the per capita income of urban and rural residents | yuan | - | |
| Proportion of social security expenditure in GDP | % | + | |
| Proportion of education and treatment expenditure in GDP | % | + | |
| Number of beds per thousand patients | beds per thousand patients | + | |
| Teacher-student ratio in primary and secondary schools | % | + |
Note: The indicators are divided into positive indicators (+) and negative indicators (-) according to their properties. A higher value of a positive indicator indicates a higher development level of the subsystem, while a higher value of a negative indicator indicates a lower development level of the subsystem. |
Fig. 2 Input and output model of decision-making units |
Table 2 Differences in the coordinated development degree of human-earth system in minority areas of Yunnan (1995-2020) |
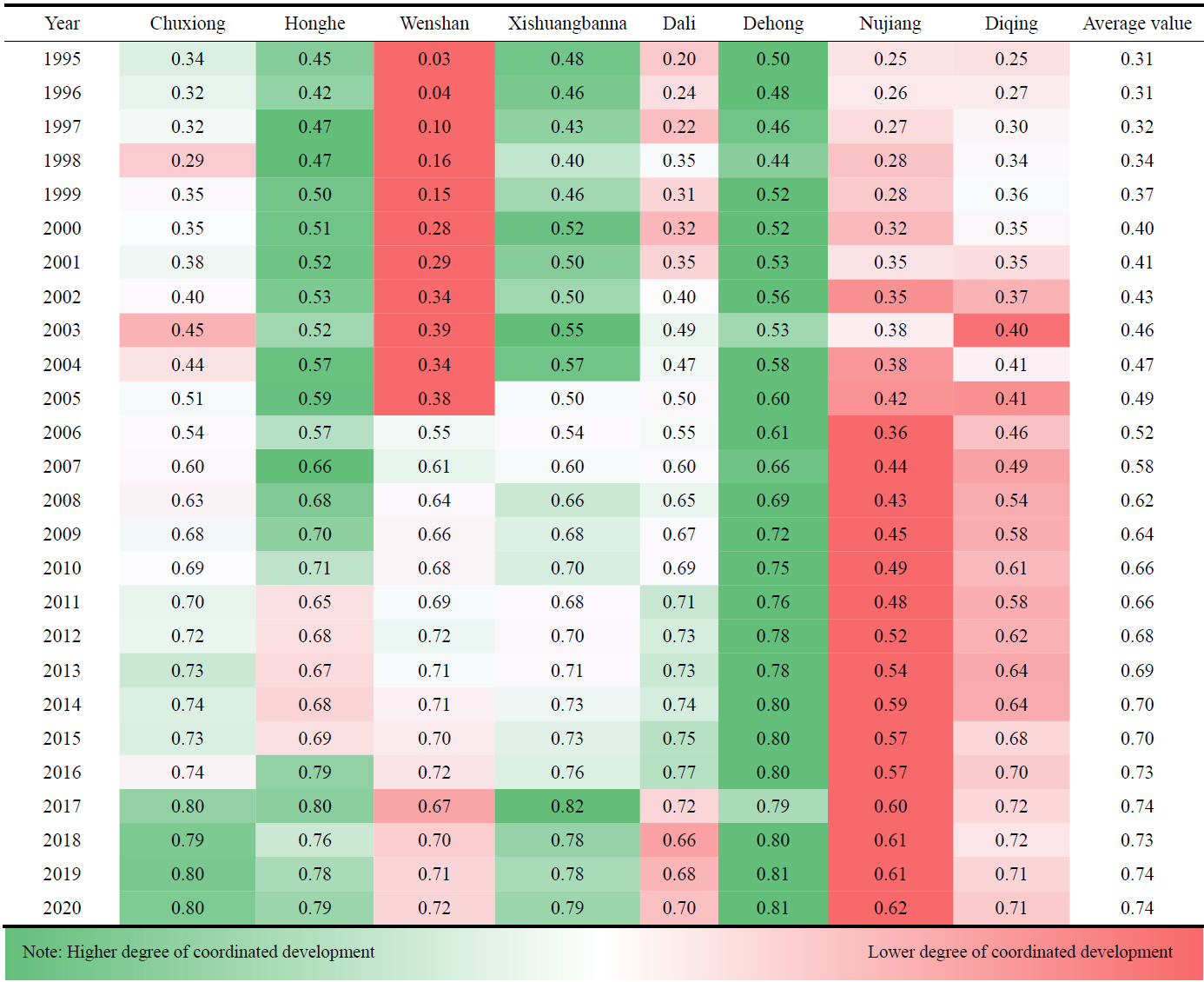 |
Table 3 Comprehensive efficiency value of coordinated development of the human-earth system in minority areas of Yunnan (1995-2020) |
| Year | Chuxiong | Honghe | Wenshan | Xishuangbanna | Dali | Dehong | Nujiang | Diqing | Number of DEA effective regions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 6 |
| 1996 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 8 |
| 1997 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 8 |
| 1998 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 7 |
| 1999 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 8 |
| 2000 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 4 |
| 2001 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 4 |
| 2002 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.88 | 4 |
| 2003 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 8 |
| 2004 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 8 |
| 2005 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 8 |
| 2006 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 8 |
| 2007 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 6 |
| 2008 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 4 |
| 2009 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 0.96 | 2 |
| 2010 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 0.81 | 0.99 | 0.64 | 1.00 | 1 |
| 2011 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 3 |
| 2012 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.85 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 4 |
| 2013 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.99 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 3 |
| 2014 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 4 |
| 2015 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 2 |
| 2016 | 0.98 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 2 |
| 2017 | 0.99 | 0.84 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 2 |
| 2018 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 3 |
| 2019 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.76 | 0.95 | 1 |
| 2020 | 0.90 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 0.96 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 1 |
Fig. 3 RMs-SMs in Chuxiong non-DEA effective years |
Fig. 4 RMs-SMs in Honghe non-DEA effective years |
Fig. 5 RMs-SMs in Wenshan non-DEA effective years |
Fig. 6 RMs-SMs in Xishuangbanna non-DEA effective years |
Fig. 7 RMs-SMs in Dali non-DEA effective years |
Fig. 8 RMs-SMs in Dehong non-DEA effective years |
Fig. 9 RMs-SMs in Nujiang non-DEA effective years |
Fig. 10 RMs-SMs in Diqing non-DEA effective years |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |