

Journal of Resources and Ecology >
Research on Ecological Carrying Pressure in the Greater Dunhuang Region based on the Relationship between Supply and Consumption
|
WEN Xin, E-mail: wenxin20@mails.ucas.ac.cn |
Received date: 2021-08-20
Accepted date: 2022-03-20
Online published: 2022-10-12
Supported by
The Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA20010202)
The National Key Research and Development Program of China(2016YFC0503505)
The Greater Dunhuang Region has experienced ecological degradation in the past 100 years caused by human factors such as ecological immigration, expansion of arable land, and the construction of reservoirs. At present, through the restoration of various ecological projects, the progress of ecological deterioration has slowed down. Ensuring that the development and construction of the Greater Dunhuang Region Cultural Tourism Economic Circle does not threaten ecological security is the top priority of the regional sustainable development plan. Based on the balance between supply and consumption of the ecosystem, this study assesses the pressure of ecological consumption in the Greater Dunhuang Region, and analyzes the patterns and trends in the ecological carrying status. The results reveal three important aspects of the ecological carrying pressure in this Region. (1) After 2000, the ecological supply in the Greater Dunhuang Region experienced a fluctuating growth trend. In the entire ecosystem, the farmland ecosystem provides more than 55% of the ecological supply, and areas with relatively high supply capacity are concentrated in a small number of valleys. (2) The Greater Dunhuang Region is under greater production pressure and there is less pressure from living consumption. The production consumption intensity has exceeded the ecological supply since 2014. The production and consumption structure of the Greater Dunhuang Region is dominated by animal husbandry production and consumption, accounting for more than 65% of the total production and consumption. (3) The Greater Dunhuang Region has been in a state of rich and surplus from 2000 to 2017. However, Dunhuang City turned into a surplus state in 2017 due to the pressure of the fast-growing tourist population. The Greater Dunhuang Region urgently needs to alleviate the ecological pressure through the development of eco-friendly industries. It is necessary to develop an ecological protection resource utilization model that focuses on the development of ecological and cultural services in pastoral areas to ease the pressure on the ecosystem from animal husbandry production.
WEN Xin , YAN Huimin , DU Wenpeng . Research on Ecological Carrying Pressure in the Greater Dunhuang Region based on the Relationship between Supply and Consumption[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2022 , 13(6) : 1048 -1057 . DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2022.06.010
Fig. 1 Land use and land cover in the Greater Dunhuang Region |
Table 1 Classification standard table for the ecological pressure state |
| Ecological Pressure State Index | <0.6 | 0.6-0.8 | 0.8-1.0 | 1.0-1.2 | 1.2-1.4 | >1.4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological pressure state | Rich and surplus | Surplus | Balance | Critical overload | Overload | Severe overload |
Fig. 2 The structure, changes and spatial distribution of ecological supply in the Greater Dunhuang Region from 2001 to 2015. |
Fig. 3 The change trend of the production pressure index in the Greater Dunhuang Region from 2000 to 2017, and in 2017 by county. |
Fig. 4 The proportions of agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry production consumption at the county level in the Greater Dunhuang Region. |
Fig. 5 The urban population, rural population and tourist population living consumption at the county level in the Greater Dunhuang Region from 2000 to 2017. |
Fig. 6 The changes and distribution of the ecological pressure status levels of the counties in the Greater Dunhuang |
Table 3 Changes in population carrying pressure and production consumption pressure at the county scale of the Greater Dunhuang Region |
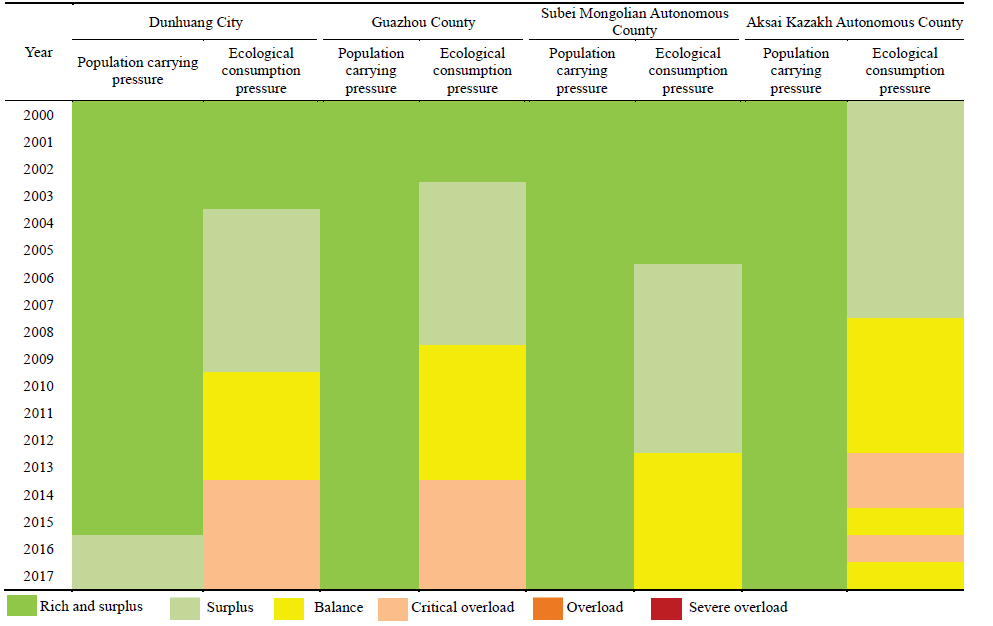 |
Note: Due to missing data for Guazhou County from 2005 to 2010, these data were obtained by SPSS interpolation analysis. |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |